Seabridge Gold has patented a process for efficiently reducing selenate species to selenide species in acidic solution using chromous ions. This method selectively removes selenium from wastewater streams by forming insoluble solids. The process ensures at least 95% reduction of selenate within 5 hours. GlobalData’s report on Seabridge Gold gives a 360-degree view of the company including its patenting strategy. Buy the report here.
According to GlobalData’s company profile on Seabridge Gold, was a key innovation area identified from patents. Seabridge Gold's grant share as of May 2024 was 15%. Grant share is based on the ratio of number of grants to total number of patents.
Continuous removal of dissolved selenium from wastewater using chromous ions
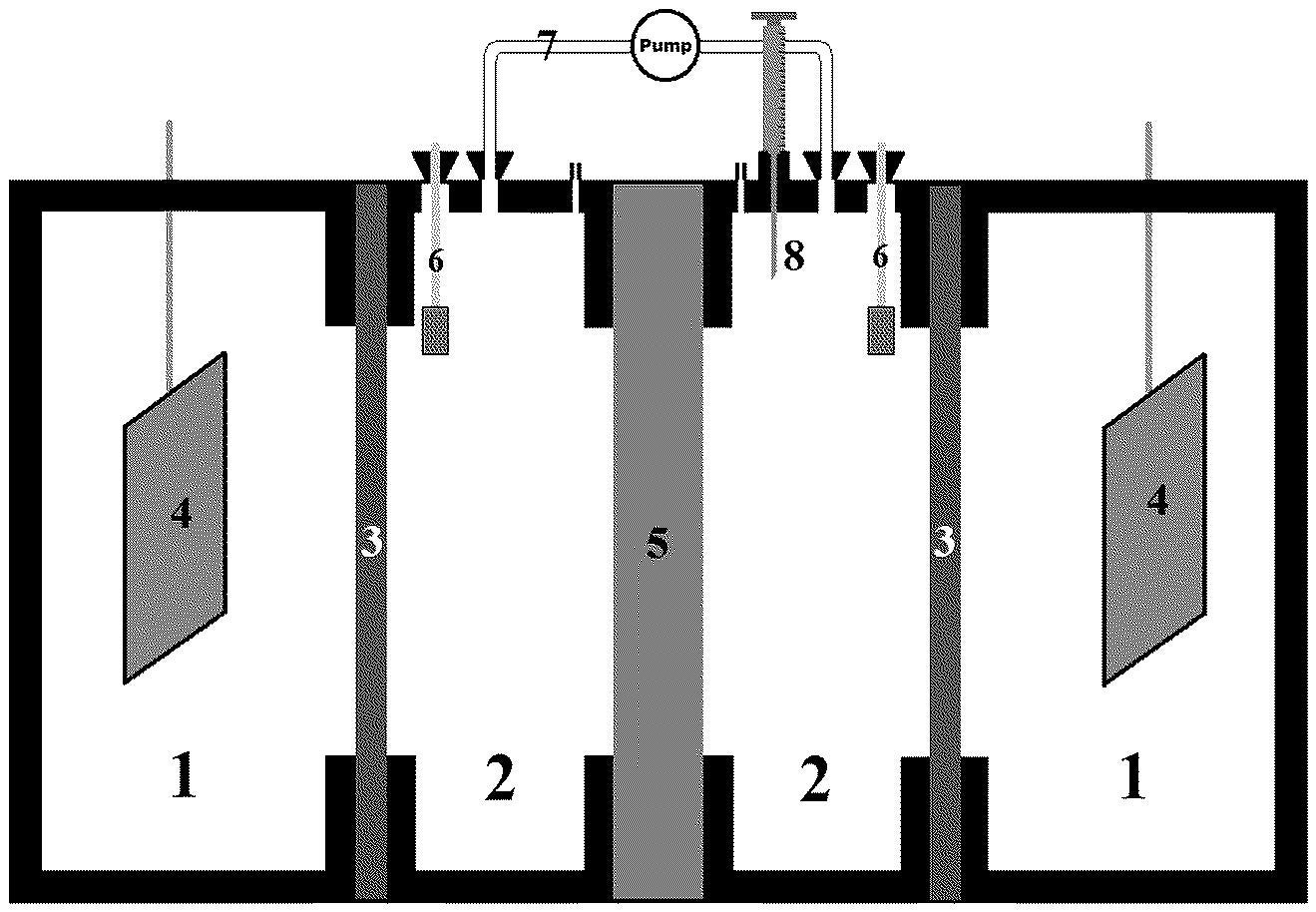
A recently granted patent (Publication Number: US11958764B2) discloses a process for continuously removing dissolved selenium species from water containing aqueous selenate (Se(VI)) by reducing it with chromous (Cr(II)) ions in an acidic reduction medium. The process aims to achieve at least a 95% reduction of Se(VI) to form hydrogen selenide (H2Se) within a reaction time of less than 5 hours, resulting in a lowered-Se(VI) solution with a final Se(VI) concentration lower than the initial concentration. The Cr(II) ions used in the process are recycled, enhancing the sustainability of the method.
Furthermore, the patent claims specify various aspects of the process, including achieving a reduction of at least 99% of Se(VI) within a reaction time of less than 4 hours, operating at an initial Se(VI) concentration of less than 100 ppm, and maintaining a final Se(VI) concentration below 5 ppm. The reduction medium is described to contain dissolved sulphate at a concentration of 10 to 400 g/L, with the reduction by Cr(II) ions being selective for Se(VI) over sulphate. The process is carried out at temperatures between 10-30°C and at a pH below 2.2, ensuring efficient removal of Se(VI) from the water stream. Additionally, the patent includes details on generating Cr(II) ions through chemical or electrochemical reduction methods, with a specific example involving the reduction of potassium chromium(III) sulfate dodecahydrate in a divided electrochemical cell with a graphite felt cathode and titanium mesh support.
To know more about GlobalData’s detailed insights on Seabridge Gold, buy the report here.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.



