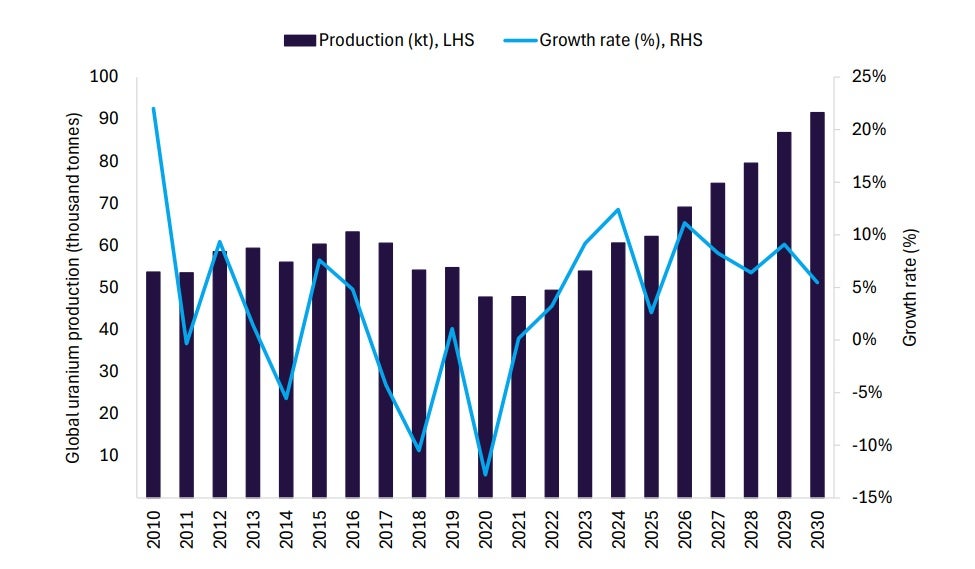
After an estimated 12.4% rise in 2024, global uranium production is projected to grow by 2.6% to 62.2 kilotonnes in 2025. Growing global concerns about climate change and the need for low-carbon energy sources, including for power-hungry data centres, have led to renewed interest in nuclear power. However, despite this positive outlook, production growth in 2025 is expected to be moderate due to temporary disruptions at major mines such as Kazakhstan’s Inkai deposit.
On 1 January 2025, operating activities at the Inkai mine were suspended due to Inkai LLP’s failure to secure the requisite approvals from the relevant authorities. This lack of essential permits compelled the company to halt production. The
production suspension was subsequently resolved later that month when the necessary paperwork was finalised. However, leading data and analytics company GlobalData anticipates this temporary disruption to result in a 2.5% decline in the country’s uranium output in 2025.
In Canada, uranium production has been significantly supported by the restart of major mines, including McArthur River. Previously shut down due to low prices and difficult market conditions, these mines have resumed operations and contributed to Canada’s position as the second-largest uranium producer, with a 23.4% share of global output in 2024.
Meanwhile, Namibia’s uranium sector is poised for substantial growth following a period of subdued production. In 2024, production reached 7.1 kilotonnes, driven by the restart of the Langer Heinrich mine. Looking ahead, a 17.5% year-over-year increase is expected in 2025, mainly due to the ramp-up at Langer Heinrich and stable output from Husab and Rossing.
Looking ahead, over the forecast period, global uranium production is expected to grow at an 8% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), reaching 91.6 kilotonnes by 2030. Several uranium projects are under development or expansion, particularly in key production regions such as Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia, positioning the industry for long-term growth as demand for nuclear energy continues
to rise.
Global uranium production expected to grow modestly in 2025, due to temporary mine disruptions
Global uranium production is forecast to grow at an 8% CAGR, reaching 91.6 kilotonnes by 2030.