Moss Mine Gold-Silver Project is located ten miles (16km) east of Bullhead City in Oatman Mining District of Mohave County in northwest Arizona. The first Phase of the project was commissioned in August 2013.
The mine is wholly owned by Patriot Gold and is being developed under an agreement between Patriot Gold and Northern Vertex Mining (formerly Northern Vertex Capital). Northern Vertex Mining has an option to earn 70% interest in the project by completing an $8.5m investment over five years, preparing a bankable feasibility study, and making a cash payment of $500,000 upon signing the agreement.
Moss Mine Gold-Silver project development details
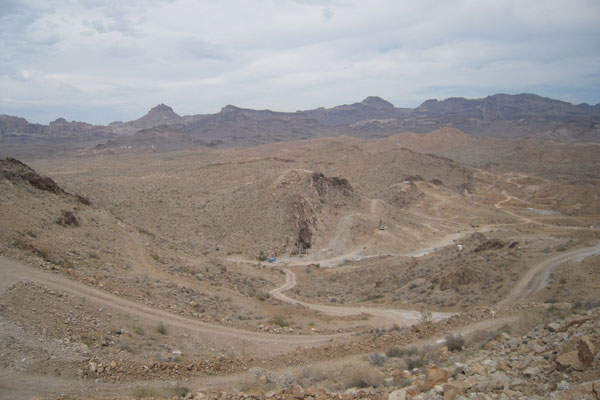
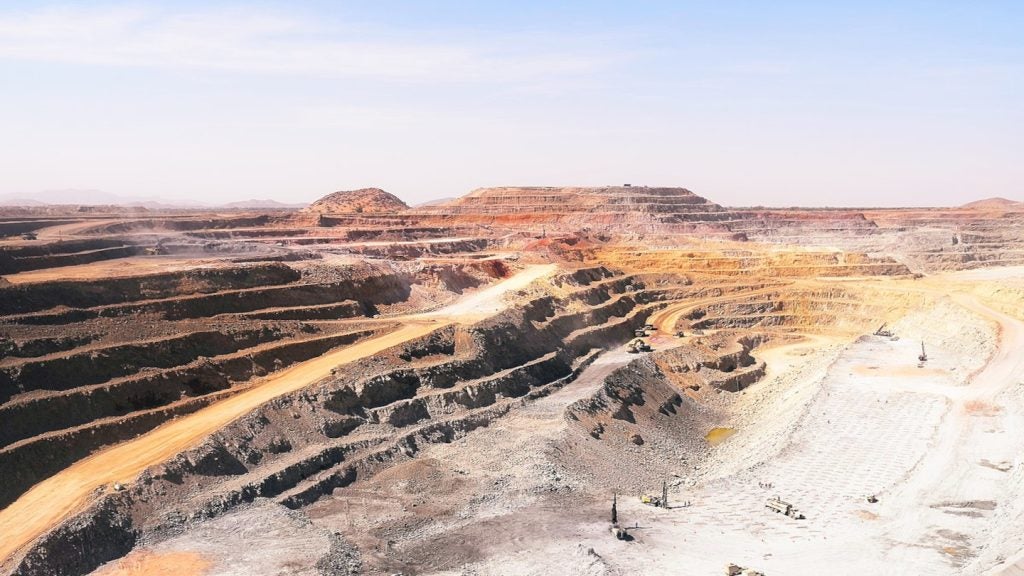
The Moss Mine Gold-Silver Mining Project is a potential heap leach, open-pit project being developed in three Phases. Phase I, which included the pilot plant, commenced mining operations in June 2013, and a total of 90,199mt of ore grading 1.404g/t of gold and 13.891g/t of silver were mined. The mined zone is approximately 500ft in length and leaching activities are currently in progress.
First, gold from the mine was poured in December 2013, and the mine life under Phase I is 15 months, assuming production rate of 1,000t of mineralised rock per day.
Phase II of the project will be carried out based on the success of the Phase I project, and will involve the mining and processing of approximately 6.13million tonnes (of measured and indicated resources) of mineralised rock. Pit depth under Phase II will range from 30ft to 575ft, and production rate under this Phase is expected to be 5,000t of mineralised rock per day. The mine life of Phase II will be five years.
Phase III will be carried out depending on the success of Phase II and will involve the extension and expansion of the mine life.
Moss mine discovery, geology and reserves
The Moss gold-silver mine was discovered in 1863, and produced high-grade gold and silver through the 1930s. It is the first major gold discovery in the Oatman District and produced 12,000 ounces of gold until it was closed in 1866. The mine was idle until the early 1980s, following which a number of mining companies, including Billiton Minerals, Magma Copper, Golconda Resources and Addwest Minerals, carried out exploration works.
The mine is founded on tertiary quartz monzonite, a coarse crystalline rock made up of quartz, plagioclase and orthoclase, which cuts into tertiary age volcanics. Precambrian basement rocks underlie the volcanics.
Mineralisation is contained within a steep to moderate dipping vein and vein stockwork zone with thickness of up to 45ft, which extends over a strike length of 1,400m. Quartz-calcite and lesser adularia are found in the veins.
The mine is estimated to contain 5.83million ounce (moz) of silver grading 8g/t Ag and 537,000moz of gold grading 0.74g/t Au, in measured and indicated mineral resources as of June 2013. The inferred mineral resources are estimated to be 801,000moz of silver grading 6.30g/t Ag and 66,000moz of gold grading 0.52g/t Au.
Open-pit mining and leach pad processing at the Moss project
The Phase I uses open-pit mining, and a leach pad measuring 700ft long and 300ft wide to process the extracted ore. The open-pit mining method involves drilling, blasting and truck shovel operations to extract the ore from the shallow gold deposit.
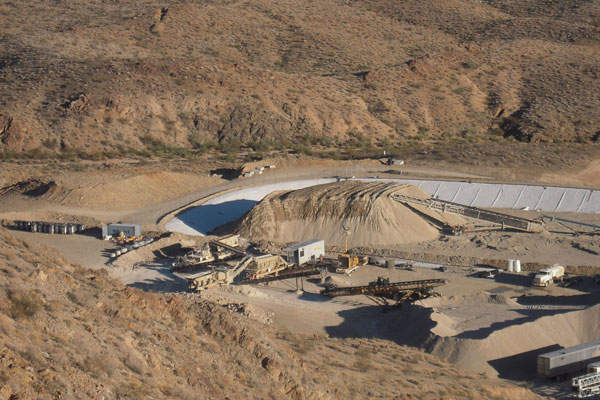
The extracted mineralised rocks are transported by haul trucks to the crushing facility near the heap leach pads, and piled.
The piled mineralised rocks are crushed to 95% less than one-fourth inch to form a fine ore in the two-stage crushing plant using high-pressure rolls grinder (HPRG). The crushed ore is then processed in an agglomeration drum unit outfitted with spray bars to moisturise and pelletise the fine ore.
The pelletised fine rocks are transferred to the heap-leach pad using radical arm stacker. The mineralised rocks are stacked in lifts with approximately 30ft thickness. Drip emitters used in cyanide solution application system penetrate through the mineralised rock heap. The precious metal is then extracted from the pregnant leach solution (PLS) using a granulated activated carbon (GAC) absorption system.
Phase II will implement the Merrill-Crowe method of processing owing to the high silver content within the mineralised rocks. It will consist of clarification filters, a vacuum de-aeration column, zinc dust addition, and precious metal precipitation. Ore will be produced by passing the filtered precipitant through a melting furnace.
Infrastructure at the gold-silver mine
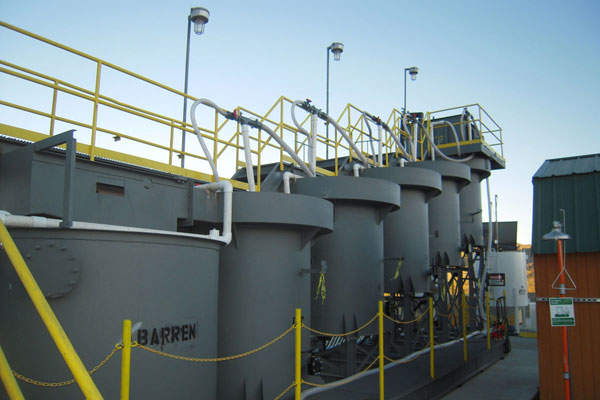
Major infrastructural facilities at the site include the heap leach pads, pregnant leach solution (PLS) and barren solution pond, and mineralised rock crushing plant. Support facilities include a power station, administration office, parking areas, storage trailers, warehouse, transmission pipelines on-site to transfer process fluids to and from the heap leach and refinery facilities, water distribution infrastructure.
Diesel and gasoline generators are being used to produce the power required for the mining operations. Approximately 1,000kW and 1,500kW of power is required for crushing, agglomeration and stacking operations of Phase I and II respectively. Another 200kW and 600kW are needed for leaching operations in Phases I and II respectively.
The mine is a zero discharge facility as wastes generated are either being reused or returned to the pit.
Contractors involved
The engineering, procurement, construction and management (EPCM) contract was awarded to CDM Smith. TRI-R Construction, Bray Construction, California Drilling & Blasting and FNF Construction were subcontracted to provide their expertise in hauling, drilling and blasting, and coarse crushing. American Steel assisted CDM Smith for the construction of the process system building.
Aggregate Custom Crushing provided the fine crushing crusher, Scotia International supplied the stackers, conveyors, jaw crushers and Merrill-Crowe System, while Process Engineering, Godwin Pumps and Phoenix Pumps supplied the process pumps.
Diesel generators, excavators, compactor and other processing equipments were supplied by United Rentals and Empire CAT. Cement silo with screw feeder was supplied by Marusi Bros.