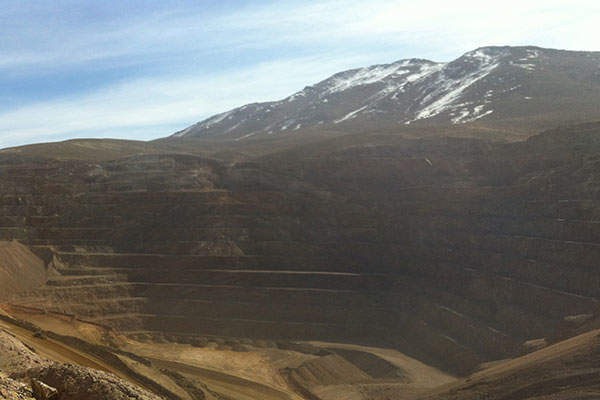
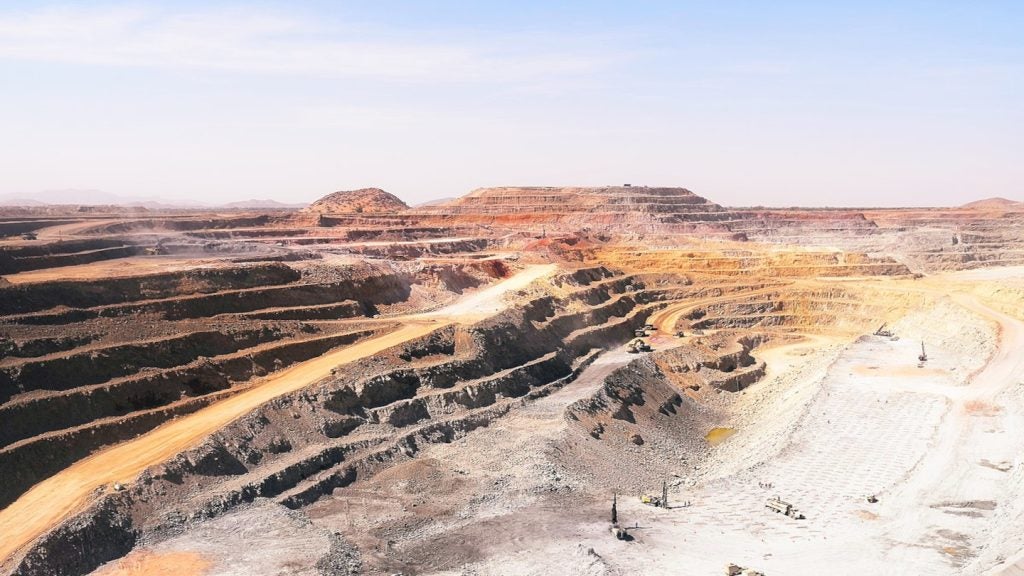
The Marigold gold mine, owned by Silver Standard, is located within the Eureka Gold Trend in Humboldt, Nevada, US. The open-pit mine has been in production since 1988 and reached the milestone of one million ounces of gold production in 2001.
Silver Standard acquired the gold mine from the subsidiaries of Goldcorp and Barrick Gold for a cash consideration of $275m.
The mine is expected to have an operational lifetime of 13 years, including nine years of active mining and four years of heap leach operation. It is forecasted to produce 1.6Moz of gold during 2015-2027.
Marigold gold mine geology and mineralisation
The Marigold project is a part of the Battle Mountain-Eureka trend located in the Battle Mountain Mining district of Nevada. The property is known to be ‘distal-type sediment-hosted gold-silver deposit’.
The mineralisation zones at the mine are tabular with the mineralised pods dipping to the west and becoming steeper in and adjacent to the normal faults. Gold mineralisation is concentrated at the convergence of these faults while sulphide mineralisation occurs in well-disposed horizons and structural locations within the sedimentary host-rocks.
The sulphide mineralisation under the influence of weather resulted in oxide mineralisation as the deposit was exposed to the near-surface environment due to uplift and erosion.
Marigold mine reserves
As of 30 September 2014, the mine is estimated to contain probable ore reserves of 129.7 million tonnes (Mt) grading 0.51g/t Au. The contained gold is estimated to be 2.12Moz.
Mining and processing of ore at the Marigold gold mine
The conventional drill and blast method of open-pit mining, along with load and haul is used at the Marigold mine. The major mining fleet includes Hitachi EH5000 haul trucks, Komatsu 930E haul trucks, Joy Global 4100 XPC rope shovels, Caterpillar wheel and track dozers, Caterpillar motor graders, and a Caterpillar 789B haul truck.
The gold project encompasses three main pit areas-Mackay, Hercules and 5 North. The Mackay pit contains 96% of the mineral resources, while the Hercules pit contains 1% and the remaining 3% is held by the 5 North pit.
The run-of-mine (ROM) ore is hauled to the leach pad by trucks and stacked in lifts. From the leach pad, the gold-bearing pregnant solution is collected in the pregnant solution ponds and pumped to carbon column trains to recover gold from the solution.
Loaded carbon from the carbon columns is transferred to the processing facility where gold is eluted from the carbon in a strip vessel. The stripped solution is mixed with sodium hydroxide and then heated resulting in a precious metal-bearing solution. The metals are separated through electro-winning and the produced sludge is retorted for mercury removal and drying.
The sludge is then mixed with flux and smelted in a propane-fired furnace for recovering final precious metal. The produced gold doré is transported by road to the Johnson Matthey refinery in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Infrastructure facilities and accessibility
Marigold is located approximately three miles south-west of Valmy in Humboldt County and is accessed by road using the Interstate Highway 80.
NV Energy supplies power for the gold project via a 120kV transmission line. Water is sourced from three existing groundwater wells near the access road to the property.
Contractors involved
AMEC Americas (AMEC) was engaged to review the adequacy of the historical quality assurance / quality control (QA/QC) methods and results.